The Importance of Risk Management Systems in Care Homes
Effective risk management is fundamental to the smooth operation of care homes. It ensures not only the safety and well-being of residents but also the operational stability and legal compliance of the facility. Care homes face various risks, such as health and safety concerns, medication errors, safeguarding issues, financial difficulties, and operational disruptions like staffing shortages or emergencies. To mitigate these risks and ensure high-quality care, care homes must adopt a structured risk management approach.
A key aspect of risk management in care homes is the use of specific documents to help guide decision-making, risk identification, and mitigation strategy implementation.
Cornerstone Care Solutions has partnered with Care England to provide members with example templates of these documents, including a Risk Matrix, Risk Management Framework, Risk Management Meeting Template, and Business Continuity Plan (BCP).
Each document plays a crucial role in identifying, evaluating, and managing risks to safeguard residents, staff, and therefore, the service as a whole. Additionally, other vital documents, such as staff training records, incident reporting policies, and resident care plans, contribute to a comprehensive risk management system. Together, these documents create a cohesive risk management infrastructure that helps care homes navigate potential challenges.
This paper explores the importance these documents and provides a comprehensive list of other governance documents that care homes should maintain to ensure effective risk management.
Risk Management Meeting Template
A Risk Management Meeting Template is essential for ensuring that risk management discussions are structured, productive, and effective. Care homes often hold regular meetings to review identified risks, discuss mitigation strategies, and assign actions to relevant parties. The Risk Management Meeting Template standardises these discussions, ensuring that all key areas are addressed and that no important issues are overlooked.
Typically, the template includes sections for reviewing current risks, identifying new risks, evaluating the effectiveness of existing mitigation strategies, and planning for any required actions or interventions. Each meeting should have clear objectives, such as resolving issues related to patient safety, reviewing incident reports, or discussing potential operational risks, such as staffing shortages or financial concerns.
The template ensures that meetings remain focused and organised, enabling teams to make informed decisions about addressing risks. This structure also facilitates tracking risk management progress by reviewing and updating actions from previous meetings. Any emerging risks can be escalated for further attention or intervention.
Furthermore, using a meeting template ensures that risk management becomes part of the daily routine and is ingrained in the care home's culture. Multidisciplinary teams—consisting of healthcare professionals, operational managers, and external experts—can collaborate on risk identification and mitigation strategies, ensuring a holistic approach to risk management.
From a governance perspective, the template also helps create a record of discussions, decisions, and actions. This documentation is crucial for regulatory audits and inspections, as it demonstrates that the care home is actively managing risks and making necessary improvements.
Figure I: Risk Management Framework
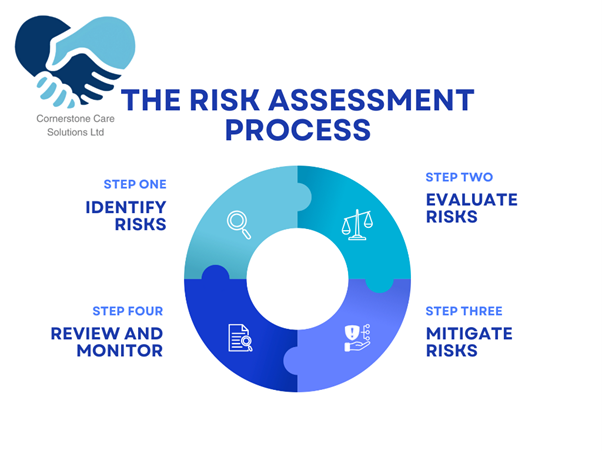
Risk Management Framework
As demonstrated in the figure above, the Risk Management Framework is a comprehensive document that defines the processes for identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring risks within a care home. It provides a structured approach to handling risk and establishes clear protocols for each step. The framework not only identifies the types of risks that may arise but also outlines the steps that must be taken to mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
A well-constructed Risk Management Framework creates consistency in risk assessment and management. It outlines who is responsible for managing different types of risks, from healthcare risks to operational or financial risks. For example, clinical staff may be tasked with managing medical or care-related risks, while senior managers may oversee operational and strategic risks. In this way, everyone in the organisation understands their role in the broader risk management process, and there is clear accountability for addressing risks as they arise.
The framework also establishes guidelines for evaluating risks, determining their potential impact, and assigning appropriate mitigation strategies. For example, risks that pose a significant threat to residents' safety—such as falls or infections—may prompt a higher level of scrutiny and the implementation of more robust prevention strategies, such as increased monitoring, staff training, or modifications to care plans.
One key benefit of a Risk Management Framework is that it promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Care homes should regularly review and update the framework to ensure that risk management strategies are effective and that new or emerging risks are considered. Regular audits and feedback from staff and residents help identify areas where the risk management process can be refined.
Moreover, the Risk Management Framework fosters a more proactive approach to risk management. Rather than reacting to incidents after they occur, care homes can anticipate and mitigate risks before they escalate. This proactive approach helps to safeguard residents and staff, improve care quality, and ensure the care home’s long-term sustainability.
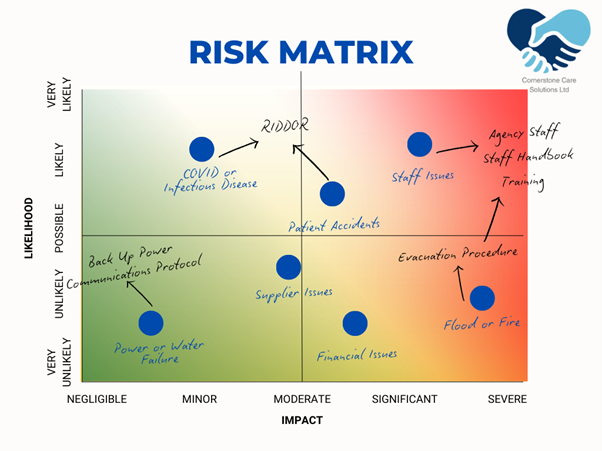
Risk Matrix
A Risk Matrix is a vital tool that helps care homes assess and prioritise risks based on two key factors: the likelihood of an event occurring and the potential severity of its consequences. By categorising risks into low, medium, high, and critical levels, the Risk Matrix enables managers to focus on the most urgent threats that require immediate attention. This visual representation of risk prioritisation, demonstrated by Figure II, simplifies the process of identifying which risks require additional resources, attention, or intervention.
For instance, a high-risk situation, such as a contagious disease outbreak or an increase in medication errors, would warrant immediate action, such as reviewing infection control protocols or retraining staff on proper medication administration. On the other hand, a lower-risk event, like minor wear and tear on equipment, may require less immediate action but still should be tracked for future attention.
The Risk Matrix also allows care home managers to make more informed decisions, as it allows them to visualise the overall risk landscape. Regularly updating the Risk Matrix ensures that new risks are continuously evaluated and that emerging threats—such as changes in regulatory requirements or evolving healthcare challenges—are promptly identified. For instance, by flagging areas of staff turnover or emerging resident needs, the Risk Matrix can guide decisions on increasing training or hiring temporary staff.
Furthermore, the Risk Matrix is a critical compliance tool. Care homes must demonstrate that they are managing risks in a structured and systematic way to meet regulatory standards, such as those set by the Care Quality Commission (CQC). The Risk Matrix serves as evidence that the service is taking proactive steps to ensure the safety and well-being of its residents, reducing the likelihood of negative outcomes and ensuring that risks are managed effectively.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
The Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a critical document that outlines how a care home will continue to operate during and after a crisis or emergency. This could involve anything from a natural disaster, such as flooding or fire, to more common challenges, like a staffing crisis or an outbreak of infectious disease. These incidents could include the ones identified in the Risk Assessment Process above. A BCP ensures that essential services continue to be provided, even when the care home faces disruptions.
The BCP typically includes contingency plans for key areas such as medical care, food provision, hygiene, and staffing. For example, during an emergency, care homes may need to implement alternative staffing arrangements, including calling in temporary workers, redistributing staff, or adjusting care schedules. It may also involve having backup suppliers for food and medical supplies in case of shortages.
A key part of the BCP is establishing clear communication protocols. Effective communication is crucial for ensuring that everyone involved—residents, staff, families, and external agencies—receives timely and accurate information during an emergency. The BCP should specify who is responsible for communicating with each group and how information will be disseminated.
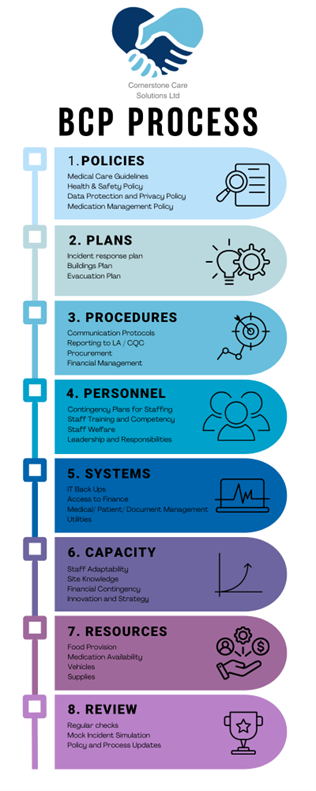
The BCP safeguards residents’ well-being and helps protect the care home’s operational integrity. During a crisis, care homes must manage multiple priorities, including maintaining safe living conditions, preventing further disruptions, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. A comprehensive BCP provides clear guidelines for managing these complex issues, minimising chaos, and ensuring uninterrupted essential care services.
Importantly, the BCP must be regularly reviewed and tested. Simulation exercises, such as disaster drills, help staff become familiar with the procedures outlined in the plan, ensuring they are prepared to act swiftly and efficiently during an actual emergency.
Recommended Governance Documents for Care Homes
In addition to the Risk Matrix, Risk Management Framework, Risk Management Meeting Template, and Business Continuity Plan, care homes should maintain several other key governance documents. These documents contribute to a comprehensive and effective risk management system that safeguards residents, staff, and the care home’s Figure III: BCP Progress reputation. Some of the essential documents that should be in place include:
Health and Safety Policy – Sets out procedures for managing health and safety risks, including infection control, equipment safety, and fire safety protocols.
Incident Reporting and Investigation Policy – Ensures that all incidents are reported, investigated, and documented, with corrective actions taken to prevent recurrence.
Staff Training and Competency Framework – Provides guidelines for staff training and professional development, ensuring that all employees are competent in risk management and care practices.
Individual Care Plans and Resident Risk Assessments – Helps assess and manage individual resident risks, ensuring that personalised care plans are in place for each resident.
Medication Management Policy – Establishes clear procedures for the safe handling, administration, and monitoring of medications.
Data Protection and Privacy Policy – Ensures compliance with data protection laws, safeguarding resident information.
Emergency Response Plans (e.g., Fire Evacuation Plan) – Defines procedures for managing emergencies, ensuring that staff and residents know how to act during crises.
Pandemic Preparedness Plan – Outlines how the care home will respond to pandemics or large-scale health emergencies.
Visitor and Safeguarding Policy – Ensures the safety and well-being of residents, particularly with respect to visitors and safeguarding practices.
Maintenance and Asset Management Log – Tracks the maintenance needs of equipment and facilities to prevent hazards.
Audit and Continuous Improvement Records
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective risk management is fundamental to ensuring the safety, well-being, and operational success of care homes. By implementing key documents, processes and practices, such as the Risk Matrix, Risk Management Framework, Risk Management Meeting Template, and Business Continuity Plan, care homes can proactively identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks. This ensures high-quality care for residents while safeguarding staff and the organisation itself. These documents not only help care homes meet regulatory requirements but also foster a culture of continuous improvement and resilience.
Incorporating additional governance documents, such as health and safety policies, incident reporting procedures, individual care plans, and emergency response protocols, further strengthens the organisation’s ability to navigate challenges. By maintaining a comprehensive set of risk management tools, care homes ensure that risks are effectively managed and that any potential disruptions are swiftly addressed, allowing for continued care without compromising safety or compliance.
Ultimately, the use of these documents ensures that care homes can provide a safe, structured, and responsive environment for residents and staff. With the right risk management framework in place, care homes are better positioned to adapt to changing circumstances, enhance the quality of care, and remain resilient in the face of potential risks or crises.
© Copyright. All rights reserved. Legal Notice Private Policy
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.

